Table Of Content
The interaction suggests that something special happens when people are tired and haven’t eaten in 5 hours. Whereas, in the other conditions, there are only small increases in being hangry. In summary, the authors’ conclusions about the efficacy of light flashes are likely to be correct (within the limits of self-reported outcomes, which they note). That said, when designing studies that address more than 1 question, when possible, one should consider the potential advantages of unconfounding those factors by conducting a factorial experiment. The advantage with this methodology is that it enables comparability between experiment/intervention groups and thus makes result analysis more efficient. But, with this methodology the covariates will need to be measured and determined before the randomization process.
The Pros and Cons of Factorial Design
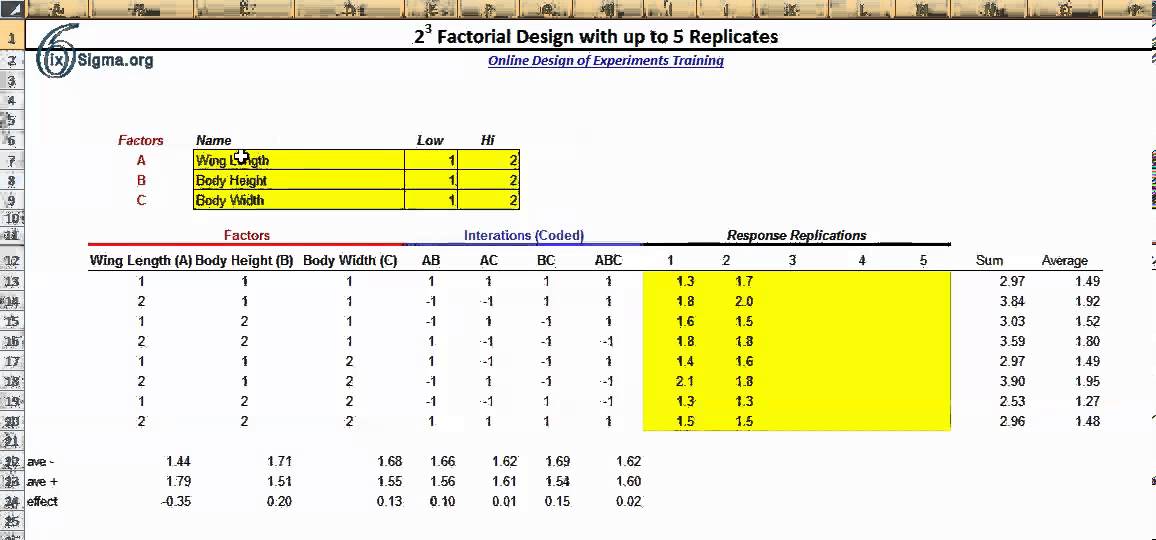
However, the limits of the model should be tested before the model is used to predict responses at many different operating conditions. After the complete DOE study has been performed, Minitab can be used to analyze the effect of experimental results (referred to as responses) on the factors specified in the design. The first step in analyzing the results is entering the responses into the DOE table. In the columns to the right of the last factor, enter each response as seen in the figure below. The additional complication is the fact that more than one trial/replication is required for accuracy, so this requires adding up each sub-effect (e.g adding up the three trials of a1b1).
IV. Chapter 4: Psychological Measurement
It is important to select the cases and controls appropriately to obtain a meaningful and scientifically sound conclusion and this can be achieved by implementing matching. Regardless of whether the design is between subjects, within subjects, or mixed, the actual assignment of participants to conditions or orders of conditions is typically done randomly. Investigators may wish to adjust ICs to enhance their compatibility with other components.
Understanding Variable Effects in Factorial Designs
Ignoring the first row, look in the last stage and find the variable that has the largest relative number, then that row indicates the MAIN TOTAL EFFECT. The Main Total Effect can be related to input variables by moving along the row and looking at the first column. To get a mean factorial effect, the totals needs to be divided by 2 times the number of replicates, where a replicate is a repeated experiment.
While more research on IC interactions is surely needed, our research has consistently found such interactions (Cook et al., 2016; Fraser et al., 2014; Piper et al., 2016; Schlam et al., 2016). Thus, it might be difficult in many cases to assume conditions that would justify the use of a fractional factorial design. This table reflects the combinations of intervention components (conditions) that is generated by the crossing of two levels of five factors in a factorial design (Schlam et al. 2016). The table shows that the crossing of the five factors generates 32 unique combinations of intervention components; participants in the experiment were randomly assigned to one of these conditions so that approximately 1/32 of the N was assigned to each condition. One of the big advantages of factorial designs is that they allow researchers to look for interactions between independent variables.
We have already seen that factorial experiments can include manipulated independent variables or a combination of manipulated and non-manipulated independent variables. But factorial designs can also consist exclusively of non-manipulated independent variables, in which case they are no longer experiments but correlational studies. Consider a hypothetical study in which a researcher measures two variables. The research then also measure participants’ willingness to have unprotected sexual intercourse. This study can be conceptualized as a 2 x 2 factorial design with mood (positive vs. negative) and self-esteem (high vs. low) as between-subjects factors. This design can be represented in a factorial design table and the results in a bar graph of the sort we have already seen.
5.2. Assessing Relationships Among Multiple Variables¶
All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies. The main effect of a factor can be defined as the change produced as a result of a change in the level of the factor. Onwards, the minus (−) and plus (+) signs will indicate whether the factor is run at a low or high level, respectively. The last four column vectors belong to the A × B interaction, as their entries depend on the values of both factors, and as all four columns are orthogonal to the columns for A and B. Frank Yates made significant contributions, particularly in the analysis of designs, by the Yates analysis.
How to classify variables in a factorial experiment design? - ResearchGate
How to classify variables in a factorial experiment design?.
Posted: Sat, 09 Mar 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Similarly, the efficacy of B is assessed by comparing cells AB and B0 with cells A0 and 00. These results may be seen as relating to the margins of the 2 × 2 table and this is why this kind of analysis is called ‘at the margins’. Cohort studies can be classified as prospective and retrospective.7 Prospective cohort studies follow subjects from presence of risk factors/exposure to development of disease/outcome. This could take up to years before development of disease/outcome, and therefore is time consuming and expensive. On the other hand, retrospective cohort studies identify a population with and without the risk factor/exposure based on past records and then assess if they had developed the disease/outcome at the time of study. Thus, the study design for prospective and retrospective cohort studies are similar as we are comparing populations with and without exposure/risk factor to development of outcome/disease.
Clinical trial
Once the design has been chosen, the "Factors...", "Options..." and "Results..." buttons become active in the "Create Factorial Designs" option menu. A traditional experiment would involve randomly selecting different tanks of fish and feeding them varying levels of the additive contained within the feed, for example none or 10%. Another important use of complex correlational research is to explore possible causal relationships among variables. This might seem surprising given that “correlation does not imply causation”. It is true that correlational research cannot unambiguously establish that one variable causes another. Complex correlational research, however, can often be used to rule out other plausible interpretations.
Some were negative health-related words (e.g., tumor, coronary), and others were not health related (e.g., election, geometry). The result of this study was that the participants high in hypochondriasis were better than those low in hypochondriasis at recalling the health-related words, but they were no better at recalling the non-health-related words. Since factorial designs have more than one independent variable, it is also possible to manipulate one independent variable between subjects and another within subjects.
Distributive randomization: a pragmatic fractional factorial design to screen or evaluate multiple simultaneous ... - BMC Medical Research Methodology
Distributive randomization: a pragmatic fractional factorial design to screen or evaluate multiple simultaneous ....
Posted: Mon, 11 Mar 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Cohort studies are study designs that compare two groups, such as the subjects with exposure/risk factor to the subjects without exposure/risk factor, for differences in incidence of outcome/disease. Most often, cohort study designs are used to study outcome(s) from a single exposure/risk factor. Thus, cohort studies can also be hypothesis testing studies and can infer and interpret a causal relationship between an exposure and a proposed outcome, but cannot establish it (Figure 4). For instance, some interactions may be due to the overall burden due to subjects receiving large numbers of components.

No comments:
Post a Comment